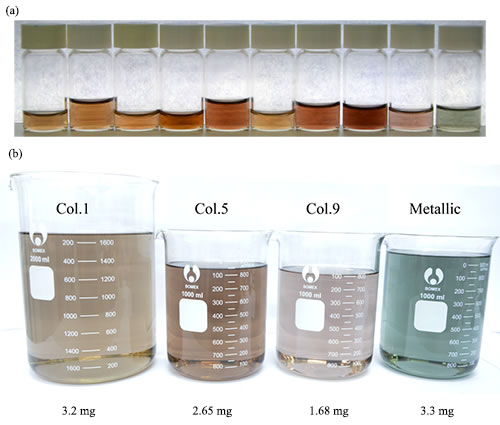
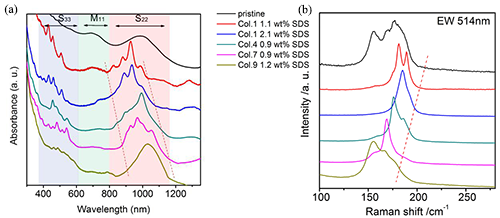
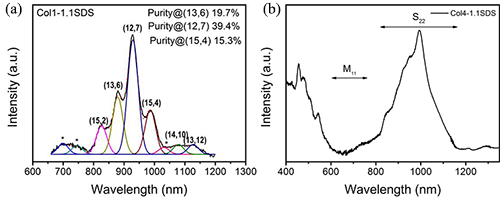
Conceptually speaking, carbon nanotubes are one-dimensional tubular molecules formed by graphene crimping. They have excellent mechanical, thermal properties, and extremely high carrier mobility, and show structurally adjustable electrons. Photoelectron characteristics have important application prospects in building next-generation high-speed, low-power, high-integration electronic and optoelectronic integrated circuits. However, the nature of carbon nanotubes is determined by their structure. Small differences in the arrangement of atoms will lead to great differences in their properties. Therefore, the control of the structure of carbon nanotubes is a precondition for the study of its properties and applications, and it is also a hot and difficult topic in the field of nanoscience and technology research. Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences / Researcher Liu Huaping, Advanced Materials and Structure Analysis Laboratory, National Center for Condensed Matter Physics, Beijing, China, devoted to the separation of carbon nanotube structure, development of gel chromatography to achieve a variety of single chiral carbon with a diameter of less than 1nm Separate preparation of nanotubes. In recent years, the interaction between temperature, ethanol, and a variety of surfactant molecules has been used to control the interaction between different helical carbon nanotubes and gels at the molecular scale, and the separation efficiency of single chiral carbon nanotubes has been greatly improved. Based on this, using the specific luminescent and photo-responsive properties of the chiral enriched carbon nanotubes prepared by separation, in collaboration with Professor Peng Lianmao’s research team of Peking University, the two-dimensional and three-dimensional carbon nanotubes were integrated for photoelectric integration for the first time. Loop. However, the diameter of carbon nanotubes prepared by gel chromatography is less than 1 nm. The separation of single chiral carbon nanotubes with diameters greater than 1.2 nm has been a worldwide problem. With the increase of the diameter of carbon nanotubes, the types of carbon nanotubes with the same diameter increase, and the difficulty in separating the structure of carbon nanotubes increases. However, theoretical studies show that in the application of high performance transistors, the best semiconductor carbon nanotubes have a diameter in the range of 1.2-1.7 nm. Recently, the research group graduate students Yang Dehua, Hu Jinwen, researchers Liu Huaping, Zhou Wei, Academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences Si Sishen used NaOH to regulate the adsorption of surfactant molecules on the surface of carbon nanotubes, and expanded the structure between large diameter carbon nanotubes and polysaccharide gels. The difference in force enables the structure separation of large-diameter carbon nanotubes (diameter>1.2 nm), and the chiral purity of the separated semiconducting carbon nanotubes can be as high as nearly 40%, the semiconductor purity can be higher than 99%, and the optical characterization confirms the above Experimental results (Figure 1-3). This method inherits the advantages of simple, rapid, low-cost and easy-to-scale separation of carbon nanotubes by gel chromatography. Through process optimization, separation yields can be as high as milligrams. The research results provide material guarantee for the preparation of high performance large-area carbon nanotube integrated electronic devices and infrared optoelectronic devices, which lays the foundation for the further separation of single-chiral large-diameter semiconductor carbon nanotubes. Related work was published on Advanced Functional Materials. The research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Frontier Science Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the “Thousand Talents for Young People†program of the Central Organization Department and the “Hundred Talents Program†of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Figure 1. Optical photographs of separately prepared aqueous solutions of different structures of carbon nanotubes. (a) Separated solutions of micrograms of MWCNTs; (b) Optimized process parameters, macro-dispersed CNTs solutions (marked below for each CNT content in the dispersion). Figure 2. Spectral characterization of a separately prepared carbon nanotube solution. (a) Characterization of light absorption spectra; (b) Characterization by Raman spectroscopy (excitation wavelength 514 nm). Figure 3. Evaluation of the purity of carbon nanotubes prepared separately. (a) Chiral purity evaluation. The chiral purity of the separated carbon nanotubes can be calculated to be nearly 40% by the fractional peak fitting; (b) The purity of the semiconductors can be as high as 99% or more. (Calculated by the area ratio of the S22 semiconductor absorption peak to the metal tube absorption peak M11). Din6330 Hex Nut,Hexagon Nuts In Stock,Oem Stainless Steel Hexagon Nuts,Fasteners Stainless Steel Hexagon Nut Chuangtuo Jinggong (Jiangsu) Co., LTD , https://www.chtofastener.com