Recently, Tang Yongbing, a researcher of the Functional Thin Film Materials Research Center of the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his team members, together with Professor Lightfoot of St. Andrews University in the United Kingdom, Sun Chenghua, a professor at Swinburne University of Technology in Australia, and Cheng Huiming, a researcher at Tsinghua-Berkeley Shenzhen Institute Successfully developed a new lithium ion battery cathode material with dual anion and cation electrochemical activity. This work has important reference significance for the research of new energy storage devices and related materials based on multiple electrochemical reaction active centers. Related research results An oxalate cathode for lithium ion batteries with combined cationic and polyanionic redox ("A oxalate cathode material with cation and polyanion redox activity" has been published online in "Nature-Communication" Communications, 2019, DOI: 10.1038 / s41467-019-11077-0). With the rapid development of key industries such as portable electronic equipment, electric passenger tools, and energy storage, lithium-ion batteries have been forced to have higher performance indicators. However, just like the bucket effect, the shortcoming of the performance of lithium-ion batteries lies in the positive electrode. Therefore, the design and development of positive electrode materials is the current research focus. Traditional lithium ion battery cathode materials mainly include oxide and polyanion. Among them, the oxide cathode such as lithium cobaltate has two redox pairs of transition metal and oxygen anion, so the capacity is relatively high. However, the electrochemical reaction of the oxygen anion is unstable, which easily generates gas and causes the cathode structure to collapse, which causes Battery failure and serious safety accidents. The polyanion positive electrode such as lithium iron phosphate significantly improves the structural stability of the material due to the polyanion as a structural framework, but the polyanion as an inactive component reduces the overall energy density. Therefore, if a new cathode material can be developed, the advantages of the two reaction mechanisms can be effectively combined, and it is expected that both high safety and high energy density will be achieved. Based on the above considerations, Tang Yongbing and his team members Yao Wenjiao, Zhou Xiaolong and others within the United Nations successfully developed a new type of Li2Fe (C2O4) 2 polyanion cathode material, and found for the first time that the polyanion cathode material has both iron ion and oxalate groups Two electrochemical activities. The reversibility of Fe2 + / Fe3 + changes was verified by the Mössbauer spectrum and the in-situ synchrotron near-absorption side and extended absorption side fine structures; the in-situ Raman spectroscopy and the near-side absorption side structure verification of carbon and oxygen synchrotron radiation The reversible change of the oxalate anion group is given; further theoretical calculations give the electrochemical reaction mechanism of the new cathode material. The study found a new type of polyanion cathode material with anion and cation dual electrochemical activity, which has important guiding significance for the development of secondary battery cathode materials based on multiple electrochemical active centers. Hospital Elevator,Escalator Brand Name,Best Hospital Elevator,Elevator Price MAURER TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. , https://www.maurer-elevator.com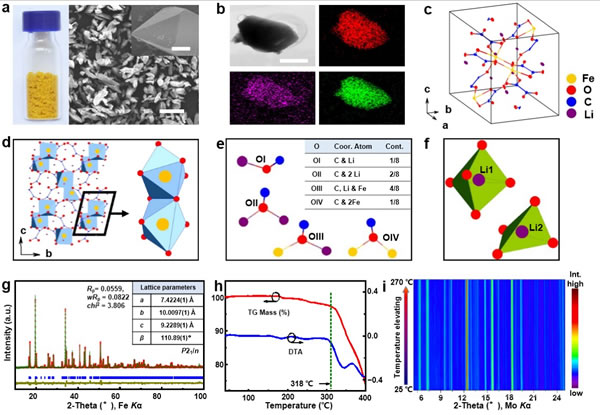
Figure: Characterization of new cathode materials (a, b), crystal structure analysis (cf), purity (g), and thermal stability performance (h, i)