
Engineering vehicles have high working intensity, complicated working conditions and poor working environment. Therefore, some key components that are commonly used must adopt appropriate heat treatment methods to improve their comprehensive performance such as strength and wear resistance. Under normal circumstances, the main heat treatment parts of engineering vehicles include shafts (sets), gears, large welded structural parts and forks, etc. This paper describes the development trend of heat treatment methods and technical applications of the above parts.
Shaft (set) parts heat treatment
The commonly used bushing parts for engineering vehicles are 45 steel, 20CrMnTi, 20CrMo, 40Cr and 42CrMo. The heat treatment method is mainly based on the carbon content of the material. The low carbon (alloy) steel is generally treated by carburizing and quenching, medium carbon ( Alloy) steel is generally treated with quenching and tempering.
Quenching and tempering
Since many engineering vehicle parts require high strength and reliability, general shaft and sleeve parts are required to be quenched and tempered. At present, construction machinery quenching and tempering parts are generally processed along the steps of forging, normalizing, quenching and high temperature tempering. Quenching and tempering treatment has always been regarded as the most reasonable process, but there are also some shortcomings, such as complicated process. And higher costs.
After the quenching and tempering treatment of the engineering vehicle parts, specific requirements should be met: that is, before the tempering after quenching, the surface metallographic structure should be martensite or bainite. When the diameter of the part is smaller than the critical diameter of the used material, the gold after quenching and tempering The phase structure should be tempered sorbite; where the diameter of the part is larger than the critical diameter of the material used, fine pearlite and free ferrite are allowed in the core after quenching and tempering. After the parts have been tempered, the surface hardness fluctuation range shall comply with the requirements of the attached table.
Surface hardness allowable fluctuation range after tempering treatment of engineering vehicle parts 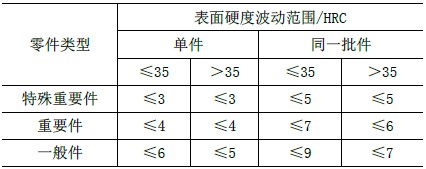
2. Forging and quenching
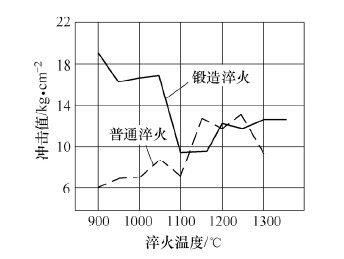
At present, in the context of advocating a proposed conservation-oriented country, forging quenching for the purpose of saving energy and improving heat treatment performance is gradually being widely adopted. The forging and quenching process is slab heating, pre-rolling, die forging, trimming, quenching and tempering. The billet heating is generally heated by induction, so it does not cause too much pollution and the working environment is good. Since the forging quenching directly quenches the residual heat after forging, the second heating process is omitted, and the hardenability of the workpiece after forging and quenching is good, and even the low alloy steel can be replaced, so that the core can be sufficiently hardened, and Very good toughness. Forging quenching and ordinary quenching impact values ​​are shown in Fig. 1. The toughness of the parts after forging and quenching is enhanced, and the fatigue strength is improved.
3. Surface induction hardening
In engineering vehicles, some medium-carbon steel shaft parts are generally or partially heated by a high-frequency, medium-frequency or super-audio surface quenching heat treatment process. The high-frequency quenching only heats at the required part, requires less energy, and has less pollution. Therefore, its application range is expanding day by day, which is an ideal heat treatment method. After the parts are quenched by high frequency heating, the fatigue strength and wear resistance are greatly improved. Some medium carbon steel engineering vehicle parts such as axles, steering knuckles, etc., after surface high-frequency heating and quenching, the cost is greatly reduced and the strength is improved. In addition, for some transmission parts such as gear shafts, surface induction hardening will also be used as the final heat treatment to enhance the mechanical properties of the tooth surface or key parts.
Before using high, medium frequency or super audio quenching, medium carbon steel and medium carbon low alloy steel should generally be pretreated with quenching and tempering to obtain good comprehensive mechanical properties.
4. Soft nitriding treatment
Gas soft nitriding treatment can greatly improve the fatigue strength, wear resistance and seizure resistance of parts, which is an important treatment method. NH3 and endothermic gas Rx (preparative gas of butane and propane) are used, and are introduced into the furnace at a ratio of 50:50, and treated at 570 ° C for 3 to 4 hours, and a compound layer of 10 to 20 μm can be obtained on the surface of the steel or cast iron. 0.1 to 0.5 mm diffusion layer.
The parts of the engineering vehicle are treated with soft nitriding, such as crankshaft, camshaft and rocker arm. Some cast iron parts also use this method to enhance their thermal fatigue resistance. Soft nitriding treatment is a treatment method to improve wear resistance. is widely used.
Ball Valve,Pvc Ball Valve,Ball Check Valve,Threaded Ball Valve
Haogong Valve Co Ltd , https://www.haogongvalve.com